Diamonds are a luxury forever! The production of diamonds today is more than the actual demand of the society. To avoid the reduction in prices (as a natural result of demand< supply mechanism), huge diamond cartels like De Beers control the supply of rough diamonds.
These cartels also keep in check the mining, processing and marketing of rough stones. After the rough stones are mined, they are parcelled to sight holders (the selected companies) for millions ofdollars.
The four C’s that determine the value of a diamond are:
1. Colour
Gemological Institute of India (GIA) has a colour scale for diamonds that ranges from D (Colourless) to Z (light yellow or brown). Colourless diamonds are in fact extremely rare. And most diamonds used in the jewellery have tints of yellow and brown.

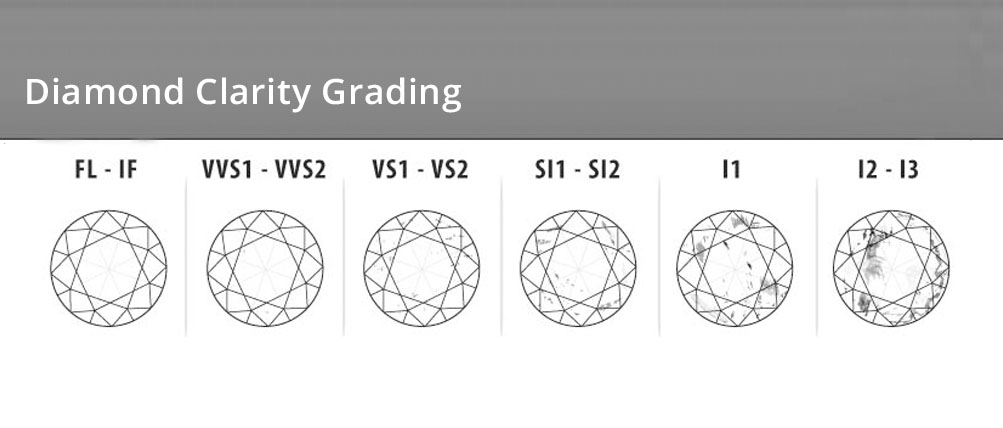
2. Clarity
GIA also has clarity scale ranging from Flawless to 13. Diamonds are rarely flawless or internally flawless, because of the tremendous heat they are formed under. Inclusions and blemishes in a diamond are natural to its formation.
Inclusions are the imperfections formed inside the Diamond and Blemishes are on the surface.
3. Cut
A diamond’s beauty is in its harmony with the light it reflects – the way the light entersand reflects offthe surface.
Brilliance is an essential component of the beauty of a diamond. It consists of brightness and the contrast created when observed ‘face up’.
Fire is the light that appears as flashes of rainbow colours.
Steep crown angles and small tables (‘old cut’ diamonds) produce more fire.
Scintillation is the flashes of light created when the diamond, the light or the observer shifts.
4. Carat
1 carat = 200 milligrams. 1 carat is considered 100 points
Cost = Carat Weight x Diamond Price Per Carat
You must be thinking: “How do I arrive at thereliable price per carat?”Well, the widely used price sheets in the diamond industry originate from Rapaport and IDEX.
Get premium quality diamonds from KGK, direct from source.